
Hernias are protrusions through a weakness in the abdominal wall or in case of hiatal hernia, through the diaphragm. The protrusions are covered by the internal lining of the abdominal cavity, called the Peritoneum. Contents of the abdominal cavity push through this defect to lie in the sac in the erect posture and reduce back into the abdominal cavity on lying down or on gentle pressure.
A Hernia can happen at any age. You may be born with a hernia (Congenital) or it may be acquired from acute or repetitive muscle stress or strain. Both men and women can get a hernia.
There are several different types of hernias depending upon their location in the body. They may be present at birth or develop later in life. Hernias by themselves may be either asymptomatic (produce no symptoms) or they may cause slight to severe pain. When the contents of the hernia bulges out, it can apply enough pressure that blood vessels in the hernia become constricted and the blood supply is cut off (Strangulation). This often leads to life-threatening conditions such as gangrene or peritonitis and may also result in the intestines becoming blocked (Obstruction) This would require life -saving emergency surgery.
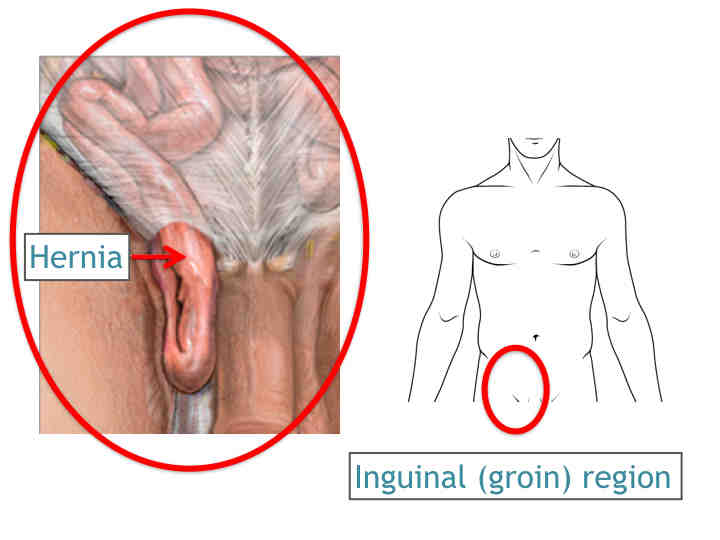
One of the most common type of hernia is Inguinal hernia. An Inguinal hernia is a lump in the groin that occurs when part of the intestine pushes through a weakness in the muscles of the abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias are more common in boys and men due to an intrinsic weakness in this area.
During pre-birth development, the testicles develop a typical pathway. Normally, this pathway closes before birth but becomes a very possible place where hernia could occur. An indirect hernia follows this pathway as it descends from the abdomen into the scrotum. People of any age may be affected by an indirect Inguinal hernia but probability of occurrence increase as people age. Mostly seen in males but can occur in females.
The direct Inguinal hernia differs in the site of occurrence, as it goes slightly to the inside of indirect hernia’s site, rarely protruding into the scrotum. This site has naturally thinner abdominal wall. This type of hernia, in contrast with indirect hernia which can occur at any age, is more prevalent in middle-aged and elderly people as the strength of the abdominal wall is greatly affected by age.
Types of surgical intervention available:
Open Surgery
Laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery
Femoral hernias occur just below the Inguinal ligament, when the abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are more common in women and tend to present as a groin lump which may or may not be associated with pain.Sometimes the femoral hernia can be pushed back into your abdomen (#004a2ducible femoral hernia), however there is a risk that the hernia can become stuck in the femoral canal and this is known as an ir#004a2ducible or incarcerated hernia. The incidence of strangulated femoral hernias is high.
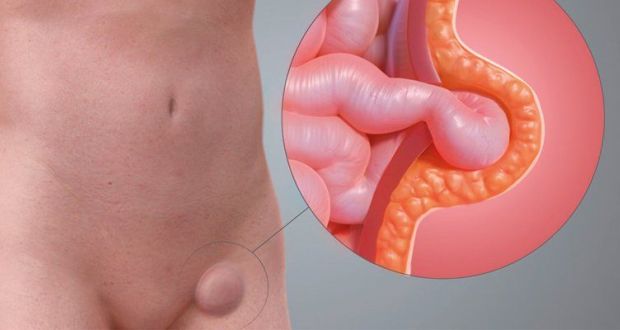
Causes of Femoral Hernia
People born with a congenital defect — one existing from birth — that causes their abdominal wall to be abnormally thin. They are at a greater risk for developing a ventral hernia. Other risk factors for a ventral hernia include:
Ventral hernias require surgical correction. If left untreated, they continue to grow slowly until they are able to cause serious complications.
Options for surgical treatment include:
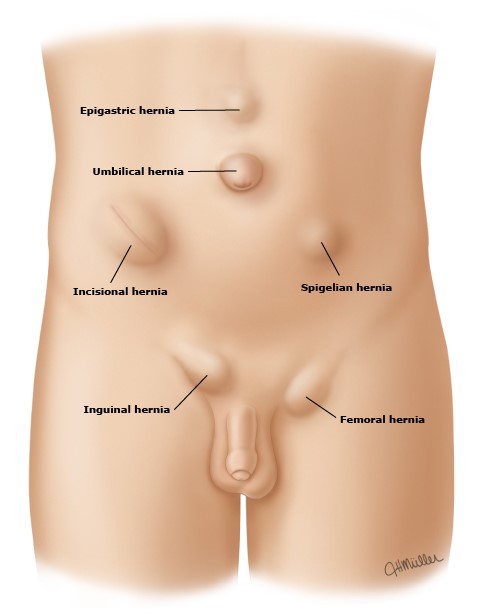
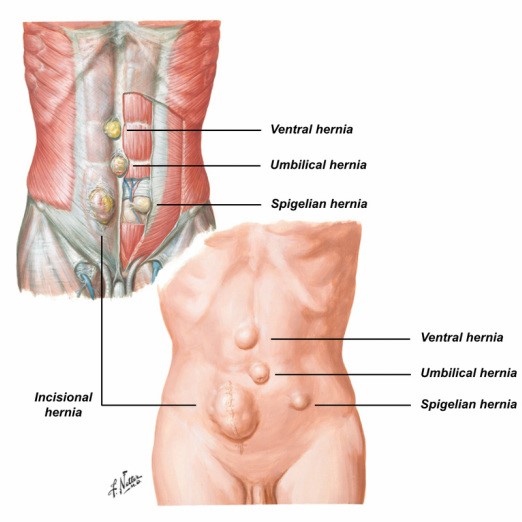
INCISIONAL VENTRAL HERNIA | UMBILICAL VENTRAL HERNIA | EPIGASTRIC VENTRAL HERNIA | SPIGELIAN VENTRAL HERNIA
Dependent upon the complexity, size and the reducibility of these hernias,
Incisional hernias are most in all likelihood to arise in obese sufferers and pregnant women. A record of multiple stomach surgeries may also boom the chance of developing an incisional hernia.
An affected person who gains substantial weight after stomach surgical procedure becomes pregnant or participates in activities that growth belly stress which includes heavy lifting is more likely to develop an incisional hernia.
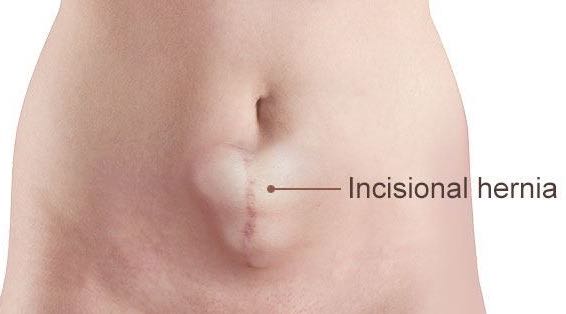
The incision is weakest and most susceptible to developing a hernia at the same time as it's far nevertheless recuperation. Incisional hernias may additionally seem to appear and disappear, that's referred to as a reducible hernia.
A hernia won't be noticeable until the affected person is involved in an activity that increases belly pressure inclusive of coughing, sneezing, straining because of constipation or lifting heavy gadgets. analysis of an incisional hernia is predominantly a scientific exam. to recognize the complex anatomy of these hernias, a ct experiment perhaps asked through your physician.
An Umbilical hernia is when the belly button pops outwards due to a weakness in the muscles around the belly button. Umbilical hernias are most common in women during or after pregnancy, or in people who are overweight.
Umbilical hernias itself is not dangerous but there is the risk that it could become incarcerated. This can cut off the blood supply to the hernia which could cause life-threatening conditions such as peritonitis or gangrene.
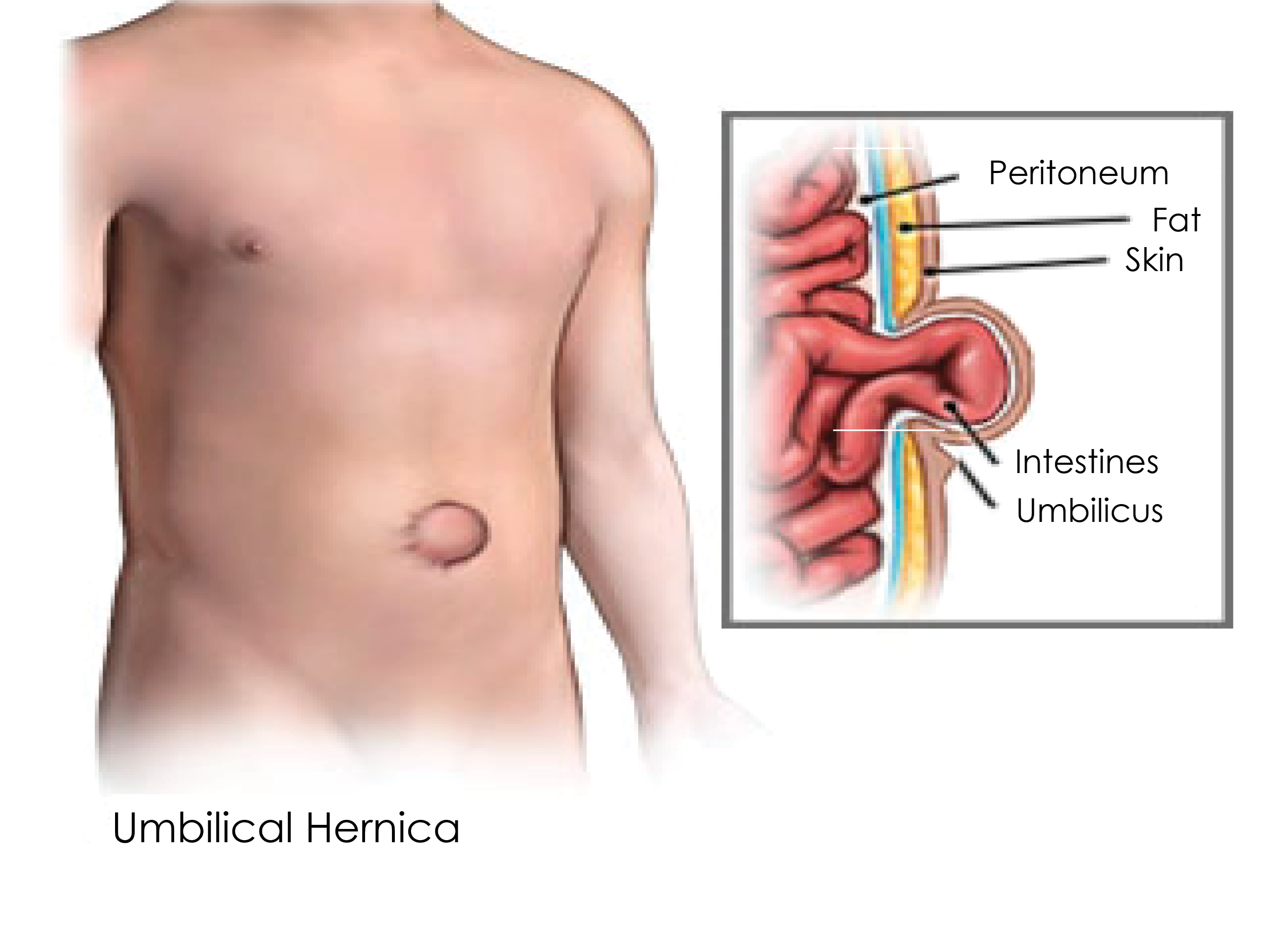
Open Repair of Umbilical Ventral Hernia
The incision is weakest and most susceptible to developing a hernia at the same time as it's far nevertheless recuperation. Incisional hernias may additionally seem to appear and disappear, that's referred to as a reducible hernia.
A hernia won't be noticeable until the affected person is involved in an activity that increases belly pressure inclusive of coughing, sneezing, straining because of constipation or lifting heavy gadgets. analysis of an incisional hernia is predominantly a scientific exam. to recognize the complex anatomy of these hernias, a ct experiment perhaps asked through your physician.
Epigastric hernias are small defects that occur in the midline, Linea Alba in the section of the abdominal wall between the lower edge of the rib cage and the umbilicus. Typically they have fatty content from the abdominal wall. The Diagnosis and treatment for this are very much the same as for the Umbilical Hernias.
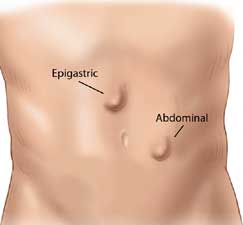
A Spigelian ventral hernia (or lateral ventral hernia) is a hernia through the spigelian fascia, which is the aponeurotic layer between the rectus abdominis muscle medially, and the semilunar line laterally. These are generally interparietal hernias, meaning that they do not lie below the subcutaneous fat but penetrate between the muscles of the abdominal wall therefore, there is often no notable swelling.
Open surgical repair of hernia
Laparoscopic (Keyhole) surgical repair of hernia
The diaphragm is a curved muscle that separates the contents of the chest from the abdomen (tummy). Diaphragmatic hernias occur when the diaphragm does no longer form completely, leaving a hole. here is an explanation about diaphragmatic hernias, how they're treated and what to expect whilst a baby involves incredible Ormond street sanatorium (gosh) for treatment.
This usually happens early in pregnancy at around six to eight weeks. The hole can be on either side, but in most children it is on the left side. You may hear the term Bochdalek hernia, which is the medical term for this type of diaphragmatic hernia. The hole in the diaphragm allows part of the intestine (gut) to move into the chest, which can squash the lungs and can stop them developing properly before birth.
Other abdominal organs can also move into the chest area, such as the liver, stomach and spleen, squashing the lungs even more.
Diaphragmatic hernias are repaired in an operation under general anaesthetic. The surgeons will only carry out the operation once a baby’s breathing and heart are stable.
Depending on the child’s size and how stable they are, the operation will either be carried out using keyhole surgery or by traditional open surgery.The surgeon would explain which approach is more likely, but there is a chance that they may need to switch from keyhole to open surgery once the operation has started.